https://www.youtube.com/shorts/QVdlXnw9mXc
Thursday, December 14, 2023
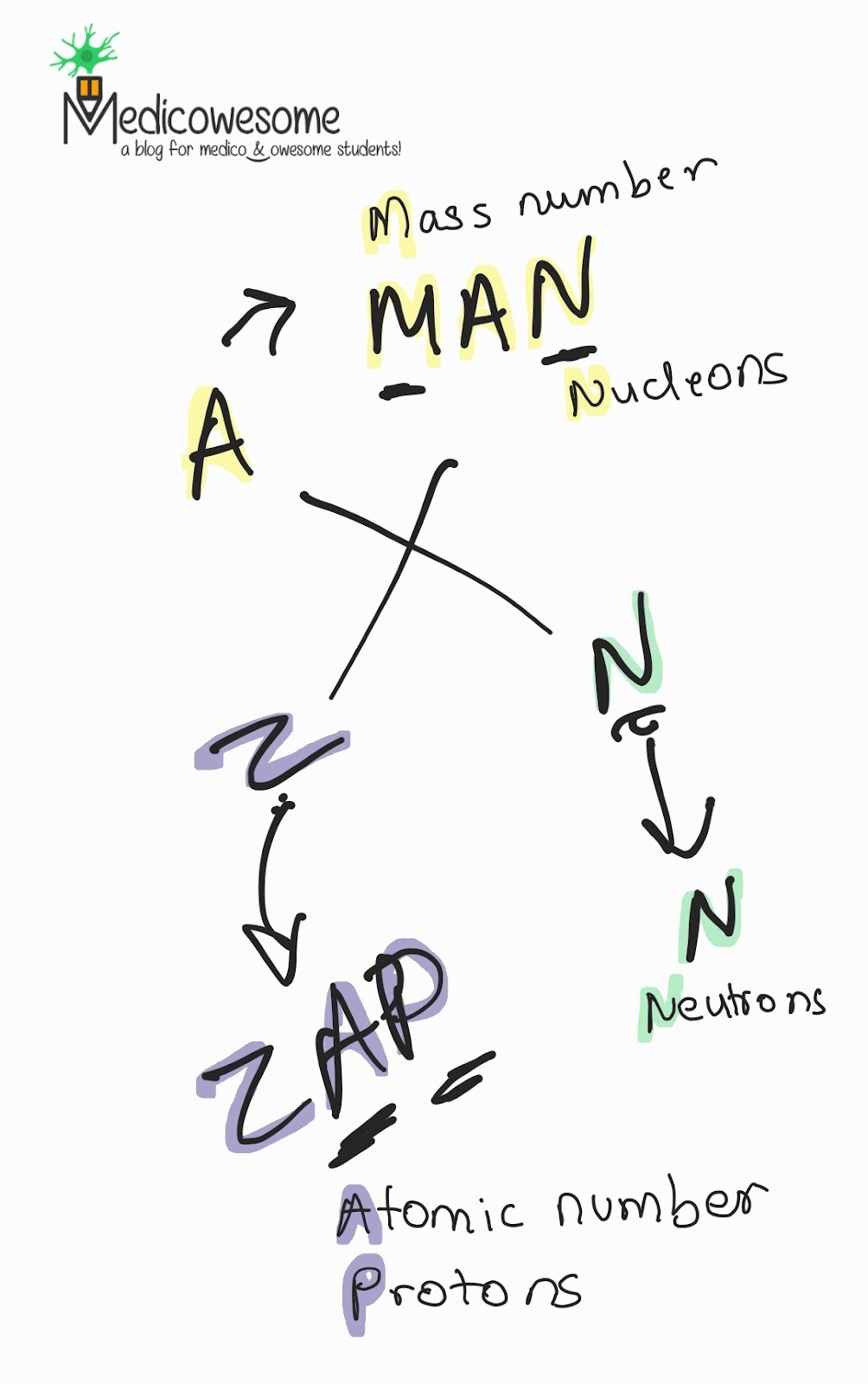
NRC dose limit for members of the public mnemonic
Wednesday, December 13, 2023
Transmission factor practice question
Tuesday, December 12, 2023
Monday, December 11, 2023
Applications of indium-111 antimyosin imaging
Applications of indium-111 antimyosin imaging:
Evaluation of the site, extent and quantitation of the severity of myocardial necrosis.
Myocarditis
Uptake after 1 year post-transplant is associated with an increased rejection rate
Anthracycline treatment - unclear role
Sunday, December 10, 2023
PET crystals
https://youtube.com/shorts/KrYSxeF0CqA?si=LdTNJd2aJc4FK0mc
LSO/LYSO has small decay time
Allows for improved coincidence timing
Friday, December 8, 2023
Linear no-threshold model in radiation safety
The most conservative theory of radiation is the "linear no-threshold" (LNT) model. According to this model, there is no safe threshold for exposure to ionizing radiation, and any amount of radiation, no matter how small, has the potential to cause harm. The LNT model assumes a linear relationship between radiation dose and the risk of adverse health effects, extending this linear relationship down to zero dose.
In other words, the LNT model suggests that the risk of radiation-induced health effects, such as cancer, increases linearly with increasing radiation dose, and there is no level of radiation exposure considered completely without risk.
Deterministic vs Stochastic effects
Deterministic effects (or tissue reactions) of ionizing radiation are related directly to the absorbed radiation dose and the severity of the effect increases as the dose increases.
Example: Cataracts
Mnemonic: DDD Deterministic severity Determined by Dose
Stochastic effects of ionizing radiation are chance events, with the probability of the effect increasing with dose, but the severity of the effect is independent of the dose received. Stochastic effects are assumed to have no threshold.
Example: Cancer
Mnemonic:
Stochastic Severity No
Probability So
Stannous ions in equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography
A small amount of stannous chloride (SnCl2) is added to a vial containing a radiopharmaceutical precursor, such as pertechnetate (TcO4^-).
The stannous ions act as a reducing agent, converting TcO4^- to a reduced form of technetium (Tc-99m).
The radiotracer, now in the form of Tc-99m, can be easily incorporated into red blood cells or other carriers.