Monday, July 25, 2022
Tuesday, June 22, 2021
Tuesday, January 14, 2020
Egg shell calcification
Saturday, November 16, 2019
Radiologic features seen in pulmonary emphysema mnemonic
Thursday, November 14, 2019
Tuesday, April 23, 2019
Think before you order a test: High resolution CT scan (HRCT)
Let's talk about HRCT today!
HRCT is the use of thin-section CT images (0.625-mm to 1.5-mm slice thickness) with a high spatial frequency reconstruction algorithm, to detect and characterize diseases that affect the pulmonary parenchyma and small airways.
HRCT cuts THIN slices.
Awesome, isn't it? Why not use an HD camera for every photograph?
Because it comes with a price!
Tuesday, February 26, 2019
Imaging Findings in PMR
Imaging —
As discussed above, there are characteristic features of periarticular structures (eg, bursitis and tenosynovitis) that can be seen on ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) . Routine radiographs do not show abnormalities in patients with PMR.
Ultrasound (US) and MRI can demonstrate synovitis of the glenohumeral and hip joints and frequent involvement of extraarticular structures, especially the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa, long head of the biceps, and trochanteric bursa. While subdeltoid/subacromial bursitis is a characteristic imaging feature of PMR, it is not specific and is seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other shoulder pathology .
Bhopalwala. H
Saturday, February 16, 2019
Grading of Sacroiliitis on Imaging
Plain radiographs of the sacroiliac (SI) joints can be semiquantitatively graded based upon the presence of the characteristic radiographic findings :
●Grade 0: Normal .
●Grade 1: Suspicious changes .
●Grade 2: Minimal abnormality – Small localized areas with erosions or sclerosis, without alteration in the joint width . Erosions usually first appear on the iliac side.
●Grade 3: Unequivocal abnormality – Moderate or advanced sacroiliitis with erosions, evidence of sclerosis, widening, narrowing, or partial ankylosis .
●Grade 4: Severe abnormality – Total ankylosis
Bhopalwala. H
Sunday, December 2, 2018
Peculiar pattern of pulmonary edema
Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Radiology series #1 X-rays 1.0
X-rays
Tuesday, May 29, 2018
MCQ mnemonics series: Mnemonic for a condition causing lower abdominal pain
2) Ischaemic colitis
3) Large bowel obstruction
4) Sigmoid volvulus
Saturday, December 9, 2017
Sunday, August 13, 2017
Diagnostic features in the X-ray and probable pathology in the Sinus
1. Haziness of sinuses only :- Sinusitis
2. Bony expansion without erosion :- Benign tumefaction e.g Polyposis
3. Decreased air shadow in nasal cavity without bony expansion :- Hypertrophic rhinitis
4. Bony erosion with expansion :- Malignancy
5. Bony defect without expansion of haziness :- Surgically induced (Iatrogenic) or fracture
6. Fluid level in maxillary sinus :- Sinusitis with pus signifying acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis
This question was asked to me by my friend and it was fun to find the answer.
(Source :-Otolaryngology at the eleventh hour By Anupam Mishra)
That's all for today.
-Upasana Y. :)
Sunday, August 6, 2017
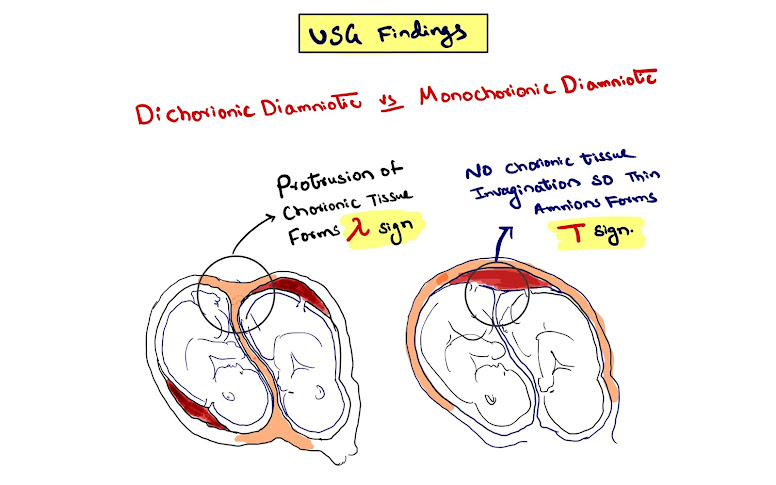
Image Based MCQ on Twin Pregnancy
#Obs_Gynae
Q. What is the diagnosis of the given USG image?
Friday, August 4, 2017
Image Based MCQ on Fracture
Yesterday we posted an Image based MCQ on Fracture of forearm bones and here's the answer for it.
Q. The X-ray of forearm in AP and Lateral views as shown in the image is diagnostic of
B. Barton fracture
C. Monteggia fracture-dislocation
D. Colles fracture
Type II: posterior dislocation of radial head
Type III: lateral dislocation of radial head
Type IV: anterior radial head dislocation as well as proximal third ulnar and radial shaft fractures
Thanks for your active participation.
Wednesday, August 2, 2017
Subpleural opacities and Ground Glass Opacities
Hey guys!
I saw a patient today, a 37 year old female patient with chief complaints of cough and shortness of breath. She has a history of allergic rhinitis and migraine. She is also obese with an BMI of 31.
As you must have guessed already she was diagnosed with Bronchial asthma. On the spirometry report done 4 months back, there was an obstructive pattern and after giving bronchodilators her FEV1 increased by 22% (>12%) and FEV1 vol increased by 300ml (>200ml). These findings also strongly support the diagnosis of asthma.
She was started on Albuterol as needed and Salmeterol-fluticasone MDI. She didn't show good response in the first 4 weeks, so she was also started on Montelukast and Tiotropium inhaler.
Now after 4 months, she still had cough and shortness of breath. She had bilateral polyphonic wheezes. A chest X Ray was done which came out to be normal. On pulse oximetry, SaO2 was 97% while breathing ambient air. On chest CT we found two attributes:
Subpleural opacities and Ground glass opacities.
So based on the CT scan findings, differential diagnosis:
Subpleural opacities:
1. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis( previously called Churg Strauss).
2. Organizing pneumonia
3. Pulmonary embolism with resultant subpleural pulmonary infarction
4. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis ( well, not really, actually in this case, there is peripheral air space opacification which looks identical to subpleural opacities)
Now Ground glass opacities:
1. Atypical pneumonia
2. Hypersensitivity pneumonia
3. Several ILDs
4. Sarcoidosis
5. Pulm Edema
6. Pulm Haemorrhage
That's all!
-VM
Sunday, July 30, 2017
Flexion Tear Drop Fracture
2. Fracture of the anteroinferior vertebral body (Tear Drop Sign)
3. Loss of anterior height of the vertebral body -Cervical kyphosis.
4. Posterior cervical displacement above the level of injury.
5. Widening of interspinous processes.
6. Intervertebral disc space narrowing.
7. Disruption of the spinolaminar line.
8. Vertebral body rotation with an AP diameter that appears smaller than on other levels.
9. Anterior dislocation of the facet joints.
Thank you.
Tuesday, July 25, 2017
Fact of the day : Reduced white matter due to depression
People ( or patients ) suffering from depression have reduced integrity of white matter substance. This means the neuronal circuit loses its connections with other parts of brain due to miscommunication between the brain cells.
A recent study mapped the internal structures of brain using diffusion tensor imaging ( DTI ) technology, that is a specialised MRI scan that creates a 3D map as it follows the diffusion of water in brain tissue.
( Source )
- Jaskunwar Singh
Monday, July 3, 2017
Ultrasonography in Acute Appendicitis
Ultrasonography ( graded compression technique ) is the investigation of choice in cases of acute appendicitis.
Saturday, June 24, 2017
Mnemonico diagnostico: Opacities that may be confused with renal calculus
Mnemonic for opacities on a plain abdominal radiograph that may be confused with renal calculus:
TOP GAME
Tubercular calcified lesions in the kidney
Ossified tip of 12th rib
Phleboliths (calcifications in the wall of pelvic veins)
Gall stones
Appendicular/ Adrenal gland concretions
Mesenteric lymph node calcifications
External (foreign) bodies in alimentary canal (ex., cyclopenthiazide)
Thats all
- Jaskunwar Singh