Monday, August 29, 2022
Saturday, August 6, 2022
Monday, July 25, 2022
Tuesday, May 3, 2022
USMLE STEP1 just changed! You need to too!
On 26 Jan 2022, the USMLE Step 1 changed its score reporting format to Pass/Fail only. This means, that those who give their exam after this date cannot see their 3 digit score, and neither can anybody else (yes, not even PDs)
Thursday, September 30, 2021
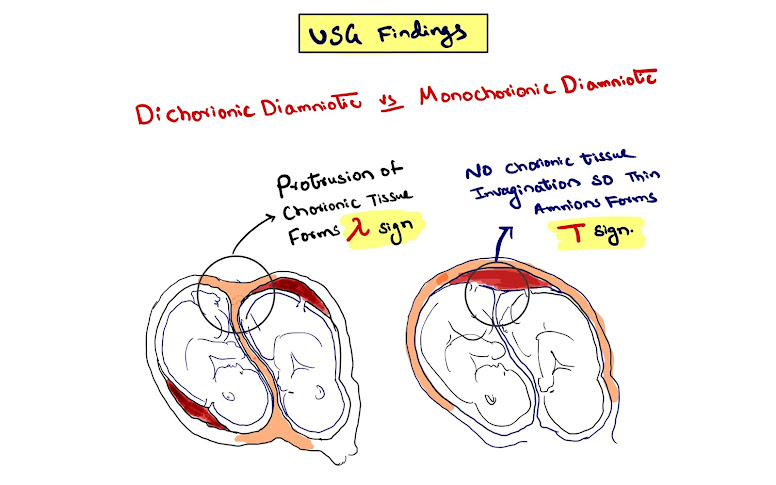
Saturday, May 29, 2021
The Happy face
Hi everyone!
Lets talk about a 2 year old girl with a h/o seizure disorder who presents to your clinic for the first time for routine care. Past medical records shows that the patient is on anti-seizure medication since the last year. There is no family history of seizures. Parents report poor feeding and sleep disturbances. The girl appears to be very happy, laughing all the time for no reason. On examination, her head circumference is in the 10th percentile and is noted to have hand flapping behavior. She has not met the expected milestones for her age. What is the diagnosis?
???
ANGELMAN SYNDROME
Fun fact: Angelman Syndrome was previously known as "Happy Puppet Syndrome"😄
- Padma Sri Katikaneni
Sunday, May 23, 2021
Ehler-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) - High yield only
Hi! So let's learn EDS together. I've tabled a list of high-yield points of all the types of EDS. It requires little bit of revision but once you get a pictorial familiarity you should be able to recall them all.
Have fun!
- They are all Autosomal Dominant.
- They have common Clinical features - skin HYPERelasticity, joint HYPERmobility and HYPER (easy) bruising.
- Go serially, Classical has the first 2, Type I and II and HYPERmobile is III and lastly Vascular is type IV
- Vascular type has additionally - arterial & uterine rupture.
- EDS types with enzyme defects are Autosomal Recessive. So, 4 and 6 are AR.
- Kyphoscoliotic EDS is Type VI (K rearranged is a V and I)
- For the last 2, mnemonic is ABCD😛 Arthrochalasia VII a, b and VII c is Dermatosparaxis.
- KyphoSCOLIOTIC EDS - defective lysyl hydroxylase (=> abnormal cross linking of collagen or KOLLAGEN => think of bones 🦴 => congenital SCOLIOSIS)
- ARTHROchalasia is COL IA (1st letter is A) and hence presents with severe JOINT hyper mobility.
- DERMATospARaxis is AR and a defective Procollagen-N-peptidase and presents with CUTIS laxa. (Cuties are Pros ;)
Saturday, May 8, 2021
Creatinine clearance in elderly - basic notes
Hi!
Elderly people have a decrease in creatinine clearance (CrCl), which means an increase in serum Cr. It is observed that annual rate of this decrease in CrCl is approximately 1 ml/min. after the age of 50 years.
Therefore, it is important to calculate the dose and dosing intervals of nephrotoxic drugs (eg., aminoglycosides) in these patients in order to prevent the precipitation of ARF.
In general,
CrCl <100 ml/min is abnormal.
However, CrCl <10 ml/min signifies the onset and worsening of acute renal failure.
Note -
• GFR is directly proportional to CrCl.
• GFR decreases by age, but not always accompanied by rise in Cr.
• Cockcroft-Gault formula is commonly referred to for calculating CrCl.
CrCl = (Ucr × V)/Pcr (~GFR)
• Double the Cr = Half the GFR.
Note that those patients with signs of worsening diabetes and resulting glomerulopathies, an increase in both GFR and CrCl is seen, which thus causes hyper filtration injury.
That's all
- Jaskunwar Singh
Friday, May 7, 2021
Simvastatin combination with fibrates in clinical practice
Hi!
High-yield in clinical practice:
DO NOT combine simvastatin with gemfibrozil (class-X interaction; high risk of acute liver damage and rhabdomyolysis). Inhibition of CYP450 enzyme by gemfibrozil plays the role in increasing levels of simvastatin 2-3x.
Combination of simvastatin with fenofibrate is relatively safer, although close observation and regular monitoring is required (class-C interaction). Serum levels of simvastatin remain unchanged.
- Jaskunwar Singh
Saturday, May 1, 2021
Lyme's disease - a review
Hi!
Lyme's disease/ Lyme borreliosis
A patient with a typical history of frequent visits to the woods with bull's eye rash, neurologic features, cardiac abnormalities, and musculoskeletal features.
Monday, April 26, 2021
Menkes disease and Wilson's disease - DDx
Hi!
Okay so maybe they are the two of the options for a patient's clinical scenario question and you have a blurred memory for which is which in context to copper metabolism?
Let's clear the basic facts here...
Saturday, April 24, 2021
Ampicillin-rash in infectious mononucleosis
Hi!
Penicillins such as amoxicillin and ampicillin are currently not recommended in patients with infectious mononucleosis with bacterial secondaries (streptococcal tonsillo-pharyngitis). Why?
Sunday, February 28, 2021
Essential tremor - a mnemonic.
Monday, February 22, 2021
Tuesday, December 15, 2020
Friday, December 11, 2020
Conus medullaris syndrome vs. Cauda equina syndrome
Both of these are orthopedic/neurosurgical emergencies! But in general, CM syndrome is more severe than CE syndrome.
Here's a comparison between the two...
Monday, November 2, 2020
USMLE STEP 1: Resources and preparation
Friday, October 9, 2020
Mechanism of action of lipid-lowering drugs
Ezetimibe inhibits cholesterol absorption from the intestine.