Tuesday, July 26, 2022
Sunday, March 11, 2018
Pulp Stones
In Pulp cavity, age changes causes
- Cellular changes
- Fibrosis of tissue
- Pulp stones or denticles
- Diffuse calcification
Cellular changes
- Number of cells
- Size of cell
- Number of Organelles
Fibrosis of tissue
- Accumulation of bundles of fibers
- In radicular pulp: longitudinal fiber bundle
- In coronal pulp: diffuse fibers
Pulp stone or denticle
- They are nodular or calcified masses
- They have calcium:phosphate ratio comparable to dentin
- They can be Single or multiple
- Present in functional and unerupted teeth
- It is present in both coronal and pulpal portion
Classification: According to structure
- Rare
- Found in the apex region
- The remnant of epithelial root sheath within pulp induce pulp cells to differentiate into odontoblast to form dentin masses
Classification: According to location
- Free pulp stone is entirely surrounded by Dentin
- Attached pulpstone is partially fused with Dentin
- Embedded pulpstone is entirely surrounded by pulp
Types of Dentin
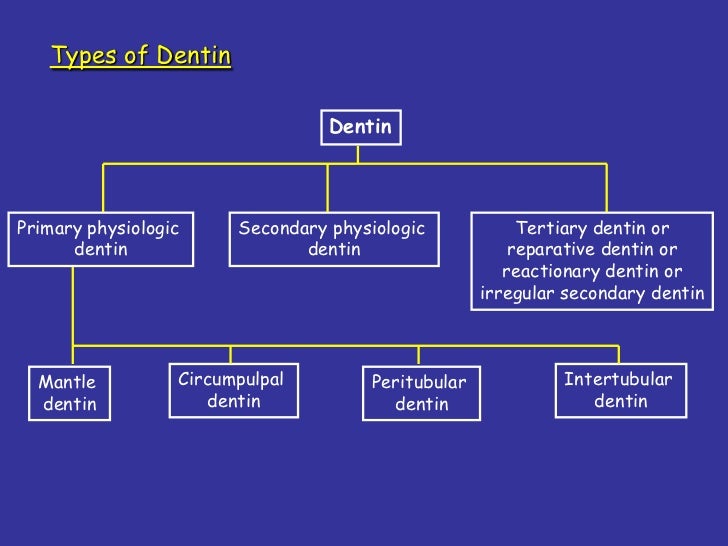
Primary Dentin
A. Mantle Dentin
- First formed dentin in the Crown
- Type III collagen
- It is less mineralized
- Matrix vesicles are present which help in Globular calcification
- It forms the bulk of the tooth
- Type one collagen
- It is more mineralized
- Matrix vesicles are present which help in Linear and globular calcification
Secondary Dentin
- It is formed after the root completion
- It contains dentinal tubules which are S-shaped
- The mineral ratio is similar to primary Dentin
- Secondary Dentin is a narrow band of Dentin bordering the pulp
- As age increases, inorganic content increases
- Therefore the Dentin becomes sclerosed
- It means It protects the pulp from exposure in older teeth
Tertiary Dentin
Abrasion
Erosion
Cavity preparation
- It is deposited on the pulpal surface of Dentin only in the affected area
- The appearance of Dentin varies as it is formed by an odontoblast
- Quality and quantity of tertiary Dentin depends on intensity and duration of stimuli
Written by Anisha Valli :))))
Tuesday, August 29, 2017
Friday, August 25, 2017
MIL: Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Right Eye
Introducing Medicowesome Image Library (MIL)
I wish to create a visual learning experience by adding images and videos along with what we write.
But since most images on Google have copyright issues, the Medicowesome authors can't use them :(
That is why, I'm asking medical students, residents and acquaintances to send me images of what they see to help create the Medicowesome Image Library (MIL).
It can be anything - a histology slide, a microbiology agar, a pathology specimen, a rash, an instrument, an x-ray - anything!
Thursday, July 27, 2017
Myopathies series -Part 5
Monday, July 24, 2017
Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS) / Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) -Part 1
Monday, February 13, 2017
Soap bubble appearance on X ray:Differential diagnosis
Hello everyone!
I always find X rays quite confusing especially when they appear same.
It's a short post about differentiating bone tumors.
Soap bubble appearance on X ray is expansile, eccentric vaguely trabeculated space having thin sharp defined sclerotic margins.
Mostly seen in bone tumors and other bone lesions.
On X ray they all appear same, only way to differentiate them is to know their location and other associated factors.
Commonly seen in
1) Aneurysmal bone cysts-
Location of ABC is Metaphysis.
It occurs in younger age group i.e less
than 20 years. So the X ray of such
patient will have non fused and
immature bone.
Preferred sites are long bones of upper and lower limb, especially femur.
2) Giant cell tumor(osteoclastoma) -
Location of GCT is epiphysis
Here the prevalent age group is 20-40, which means an adult sketetal structure.
While the preferred sites are same like ABC.
So if one see epiphyseal lesion with soap bubble appearance in mature bone, it has to be Giant cell tumor.
GCT presents with other classical signs of Egg shell crackling on palpitations.
Giant cells on histology.
Which are NOT the tumor cells. So its one of the example of misnomers. They are meant to misguide you.
Thats it :)
Stay awesome
-Khushboo
Monday, January 23, 2017
Niemann-Pick disease notes and mnemonic
Niemann-Pick disease (NPD; also called sphingomyelin-cholesterol lipidosis) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders associated with splenomegaly, variable neurologic deficits, and the storage of sphingomyelin.
Saturday, November 19, 2016
Gap Junctions and Connexin Mutations
Let's start with a brief description of Gap Junctions. Take two empty cardboard boxes, assume they are cells. Bore a hole in each one of them and then enter a small straw in it. Then arrange the two boxes(cells) in such a way that the two straws are aligned perfectly with each other and that their cavities form a continuous column, so that if you pour water in one box it should completely go into the other one without even a single drop falling in between them.
Saturday, July 2, 2016
Thursday, April 7, 2016
Dr. Thinker: USMLE STEP 1
Monday, October 26, 2015
I am finding first year MBBS extremely difficult and tough
Firstly, take a moment to congratulate yourself. You've made it to medical school! New subjects is going to be so much fun!
"I feel left behind. I'm not able to answer. What is taught in lecture is very minimalistic compared to text book."
Sunday, September 13, 2015
Thyroid carcinoma mnemonic
I made a real easy way of remembering thyroid tumors :)
Papillary carcinoma mnemonic:
Popular (Most common thyroid cancer)
Palpable lymph nodes (Lymphatic metastasis is common)
Positive I (131) uptake
Post radiation in head and neck (One of the causes)
Pops out of the capsule (Usually encapsulated but invades capsule)
Pops everywhere in the gland (Multifocal)
Positive, pleasing, perfect, parexcellence, peerless prognosis
(Excellent prognosis because it's slow growing)
[Another mnemonic is PG - Papillary, Good prognosis =D ]
Histology:
Popping eyes (Clear nuclei, Orphan Annie Eyes)
Papillary pattern
Psammoma bodies
Pseudoinclusions (Intranuclear cytoplasmatic inclusions)
Wednesday, February 18, 2015
Study group discussion: Extra books for USMLE
Could someone suggest books to use for mle step 1? Everyday someone new tells me that the kaplan book is not good for a particular subject.
Haha
BRS + Kaplan for physiology
Road map to gross anatomy
Biochemistry Kaplan (Pretty good)
Goljan for pathology
Microbiology Kaplan (more than enough)
Pharmacology Kaplan
Behavioral Kaplan + BRS + a lot of resources online and it's never enough
What about the other subsections of anatomy?
Umm which subsections? Embryology and Histology isn't high yield.
Oh alright. Neuroanatomy?
That's a pain! There are these anki flashcards I found on neuro.. I'll send you guys the link when I'm home. Thanks!
Do all brain stem sections for step 1. Any image on neuro and you need to identify the tracts/structures!
Ah. Why don't you try clinical neuroanatomy made ridiculously simple? I have heard its a recommended book for USMLE Step 1.
Ridiculously simple series is good!
Neuroanatomy one is really short and nice.
I've read the neuroanatomy book too. It's good.
Related post:
Preparing for the USMLE Step 1 exam
I have no idea about USMLE Step 1
USMLE for Indian medical students
Sunday, December 14, 2014
Pathology brain tumors mnemonic
We'll be talking about some brain tumors today.
All of the mnemonics might not work for you, so take only what you need :)




