Monday, July 25, 2022
Sunday, July 3, 2022
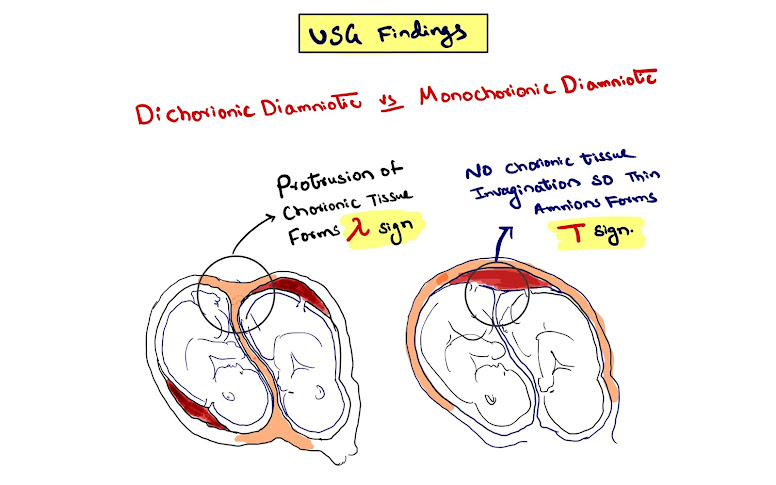
Twin pregnancy
Monday, January 10, 2022
Friday, May 28, 2021
Biophysical Profile Mnemonic
 |
| Biophysical Profile |
“ The value of experience is not in seeing much, but in seeing wisely”. - William Osler
Thank you! 🩺
Thursday, May 13, 2021
Levetiracetam - pregnancy considerations
Hi!
Levetiracetam, used primarily for seizures control, is also used off-label for SAH, status epilepticus, seizure prophylaxis in craniotomy and traumatic brain injury.
Dosing is increased in pregnancy and closely monitored regularly due to various physiologic effects, especially in third trimester. (levitate dose of levetiracetam) :-
- increased volume of distribution, Vd (increase in plasma volume, CO)
- increased renal excretion (increase in GFR; levitate the rate)
- rapid and almost complete absorption via GIT (unlike other drugs with decreased absorption in pregnancy)
- low risk of adverse effects and fetal malformations when used in monotherapy. (low with mono, high with poly)
- Levetiracetam is NOT metabolized by liver; Cyt P450 independent. Bioavailability 100%. (unlike other antiepileptics - hepatic metabolism increases in pregnancy)
Levetiracetam crosses placenta and can be detected in the newborn. (leve leaves mother)
The newborns are at greater risk of SGA and low APGAR score.
Protein-binding of the drug is low (<10%). So, decrease in albumin concentration during pregnancy does not significantly affect the drug concentration. (low pro)
That's all
- Jaskunwar Singh
Tuesday, May 11, 2021
Toxoplasmosis classic triad mnemonic
Hi!
Toxoplasmosis classic triad in neonates mnemonic: CATS
- CAlcifications (intracranial)
- Tension hydrocephalus
- See (Chorioretinitis)
Also, check out this video mnemonic by IkaN
- Jaskunwar Singh
Thursday, February 18, 2021
Monday, February 8, 2021
Contraception
CONTRACEPTION
Cu-T INSERTION
REQUIREMENTS:
Written Informed consent, IUD, Povidone Iodine, Spirit and drapes, Sims’s speculum, Allis forceps, Uterine Sound
PROCEDURE:
Begin with the history and clinical examination to rule out contraindications.
Before inserting the IUD, always do UPT to rule out pregnancy.
The patient is taken up in the OT (but can be done in OPD or labour ward immediately post-partum). An anaesthetist should be present if in case perforation occurs.
POSITION: Standard lithotomy position with legs in stirrups.
Scrubbing, painting, and draping should be done.
Bimanual examination to check for uterine size, position, version, and adnexal pathology.
Depress posterior vaginal wall with Sim’s speculum and hold the anterior lip of cervix using Allis forceps.
Using uterine sound, measure utero-cervix length and the accordingly adjust the bobbin.
The technique used is “No Touch/ Withdrawal technique”.
CuT is self-loaded. Remove the whole thing without touching CuT.

Plunger should not touch the vaginal wall. Reach upto the uterine fundus. Pull the ring behind on the plunger. CuT is unfolded.
Slowly remove the loader so as not to disturb the CuT.
Cut the tail (2.5-3 cm). The patient should be made to feel the tail.
Observe for about half an hour for uterine cramps (since foreign body inserted so uterus tries to expel it)
Managed by giving Drotaverine/Dicyclomine.
Record the date of insertion. Document it on CuT card and mention the date of expiry. Give it to the patient.
Counsel the patient regarding all the possible complications and also regarding the follow-ups.
ANTARA
Injectable Contraceptive DMPA (Under ANTARA programme) given as i.m. injection on outer upper quadrant of buttock.
Dose: 150 mg every 3 months
Written by our guest author - Ayushi Gupta
Illustration by Devi Bavishi
Sunday, February 7, 2021
Cardiotocography
CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY
CTG machine has two sensors:
Cardio probe: placed on the mother’s abdomen at the foetal anterior shoulder to measure the foetal heart rate.
Toco probe: placed on the mother’s fundus to record uterine muscle contraction.
(Jelly is to be applied between the probe and the site of application of the probe)
CTG paper moves at rate of 3cm/min
Therefore 1cm = 20 sec on x-axis
Also 1 cm = 10 bpm on Y axis
To be taken every 2 hours towards the end of pregnancy.
When analysing a CTG look for 4 things:
1. Baseline heart rate
2. Beat to Beat variability
3. Accelerations
4. Decelerations
Foetal Heart rate: Normal: 110-160 bpm
Beat to beat variability: Normal: 5-25bpm showing saw tooth pattern
Foetal accelerations:
Abrupt increase in FHR above baseline.
If a rise of 15 bpm persists for 15 sec or more but less than 2 mins is seen twice during a 20 min period then this is adequate contractions or REACTIVE (after 32 weeks).
Foetal decelerations:
Decrease of 15 bpm in FHR for ≥15 seconds
Time from onset of the deceleration to the lowest point of the deceleration >30 seconds in variable decelerations.
Early decelerations: Cause: pressure on the foetal head during labour (normal)
If late or variable decelerations are present, call a senior.
If all 4 parameters normal: REASSURING NST
If any 1 abnormal: SUSPICIOUS NST
If any 2 or more abnormal: PATHOLOGICAL NST
If CTG is non-reassuring:
Set up IV line
Start RL/Oxygen
Give left lateral position
Call the resident
Stop oxytocin
Ask sister to give OT changes/scrubs
Written by our guest author - Yash Bandewar and Anveshi Nayan
Illustration by Devi Bavishi
Monday, January 25, 2021
Mnemonic for Thanatophoric dysplasia (thanatophoric dwarfism)
Welcome!
A lethal skeletal dysplasia. It is the most common lethal skeletal dysplasia followed by osteogenesis imperfecta type II.
Mutation of fibroblast growth receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene
Type 1 : telephone handle like femurs
Type 2 : presence of a cloverleaf skull. Limb shortening milder and bowing is not there.
Mnemonic : PCR
P = Platyspondyly (flattened vertebral bodies)
C = Cloverleaf skull
R = Rhizomelic dwarfism , Rib cage is small
Rhizomelic dwarfism Proximal (i.e. femoral, humeral) limb shortening.
Present as Nonviable fetus ....so do spontaneous vaginal delivery!
Thank you!
Thursday, January 21, 2021
Mnemonic for pregnancy complications with short inter pregnancy interval
Definition : <6-18 months from delivery to next pregnancy
During pregnancy, maternal folate and iron are depleted for fetal development, and the resulting maternal anemia is exacerbated by normal blood loss during delivery (eg, up to 10%-20% of blood volume). In breastfeeding women, continued nutritional demands from the newborn prevent repletion of normal folate and iron stores, resulting in prolonged anemia!
Monday, October 19, 2020
Friday, October 16, 2020
Thursday, September 10, 2020
Naegele's formula
- add seven days (i.e 29th)
- subtract 3 months (i.e March)
- add one year (i.e 2020)