These are my notes from Harrison on Warfarin and Newer Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs).
Tuesday, August 7, 2018
Warfarin and Newer Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) notes
These are my notes from Harrison on Warfarin and Newer Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs).
Friday, August 3, 2018
Stop Antibiotic Abuse!
Hello Everyone,
It's been really long since the last post! Well it's been hectic all the way to and through residency.
I was recently researching on the topic of antibiotics while I stumbled upon this excellent piece of information cum approach by Dr.Strong on starting Anbiotics.
Well everyone should ask themselves these 12 questions before starting any antibiotic for one's patient and trust me you'll end up choosing the most appropriate one.
This is how we don't contribute to the Antibuse- "Antibiotic Abuse"( my personal neologism)
So now coming back to the questions, ask yourself these questions before you start any antibiotics,
1) What condition is being treated?
2) What are the commonly known bacterial species causing that condition?
3) Which antibiotic group is typically active against those?
4) What are the local resistance patterns for the chose antibiotic?
5)Will there be adequate organ penetration?
6) What is the preferred route of administration?
7)Any specific contraindication of the antibiotic to look out for?
8) Any required dose adjustment for coexisting renal or hepatic diseases?
9) Any specific drug interactions to be considered?
10) When on therapy anything that needs periodic monitoring?
11) How can the therapy be narrowed once bacterial sensitivities are available?
12) What will be the anticipated duration of the therapy?
Let's take a step towards stopping the rampant Antibuse.
That's all for now.
Let's learn Together!
-Medha Vyas.
Thursday, August 2, 2018
Ring-enhancing lesion in an immunocompromised host
If it is a ring-enhancing lesion in an immunocompromised host, the most commonly seen etiologies are Cerebral toxoplasmosis (50%) and Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma (30%).
But let's talk about the uncommon etiologies -
ECG quiz: ST elevation in aVR and ST depression in other leads
Sunday, July 29, 2018
Trapezius and pericarditis.
Patient explains you that the pain is radiating and he is eventually experiencing pain in to the back of this some muscle. You find out that he is pointing towards the "Trapezius muscle" .
but it never radiates to trapezius.
Upper part is supplied by the spinal accessory nerve.
Lower part is supplied by the nerves from C3 and C4 only.
Wednesday, July 18, 2018
Can you find Asterixis in Non-Hepatic disorders?
Upasana Y. :)
Thursday, July 12, 2018
Authors' diary: Ponder
Before you get a CT scan on the patient in the ER, stop and think - does the patient really need a CT scan? Will it get me the answers I'm looking for? Or will I need additional testing? Think of the harms of radiation exposure. Unless you don't want to rule out a hemorrhage that requires immediate intervention, do not order it STAT.
Tuesday, July 3, 2018
Dentinoenamel Junction
- DEJ appears as a scalloped line.
- The convexities of scallop are directed towards the dentine
- The surface of dentine appears pitted
- DEJ provides strength to the union between enamel and dentin
- Prevents shearing of enamel when functioning.
- Scalloping of the junction is seen more in the occlusal portion where masticatory stresses are high.
Enamel Lamellae
Sometimes, they penetrate towards DEJ
They consist of organic material but with a little amount of mineral content.
Types of enamel lamellae:
- Type A: Lamelle composed of poorly calcified rod segments
- Type B: Lamelle consists of degenerated cells
- Type C: Lamelle arising in erupted teeth where cracks are filled with organic material, originating from saliva
Type A is restricted to enamel
Type B and C are restricted to dentine
Clinical Significance:
- It is a site of weakness in a tooth.
- It forms a road of entry for bacteria to initiate caries.
Hunter-Schrengar bands
These bands are the functional adaptation to occlusal masticatory forces.
Alternating, light and dark bands of varying width that can be seen in longitudinal cross-section under the obliquely reflected light.
Dark bands: Parazones
Light Bands: Diazones
The angle between the bands is 40 degrees
- Written by Anisha Valli
Zone Of Weil
- Its a layer of 40um.
- It is also known as the sub-odontoblastic layer.
- It doesn't consist of cells.
- This zone is prominently seen in the coronal pulp.
- Cell-free zone decreases in size when dentin formation occurs at a rapid rate.
- The cell-free zone consists of a network of nerve fibres which lost their myelin sheath. This is known as Plexus of Rashkow.
Sunday, June 17, 2018
Mnemonics for special orthopedic tests
b) The neck is stiff from the freezing in the snow.
b) The head's side of the coin has de (the) queen embossed on it.
*Description : Internally rotate the shoulder to produce pain if rotator cuff pathology.
*Mnemonic :Imagine a hawk flying in circles (rotate) , waiting to attack the shoulder of its prey.
*Description : Passive forward flexion of head causes electric sensation down the spine.
*Description : With shoulder at 90 degrees flexion, instruct patient to point thumb at ground and resist downward force. Repeat with palm facing upwards.
*Mnemonic : a) This is a story of O'Brien who worked as a labourer.
b) He got thumbs down for his work.
c) So he had to beg (with palms facing upwards) to make end's meet.
b) Imagine if there are spurs formed in spine, they will compress the spinal cord causing radiculopathy.
b) Imagine Andy Murray to be suffering from meniscal tear.
c) Also Mc Murray and meniscus both have M and C.
*Description : Instruct patient to bring dorsal aspect of hands together.
*Significance : Tingling or paresthesia in lateral 3.5 fingers suggests carpal tunnel syndrome.
b) The handcuffs are tight and compressing his median nerve causing tingling and numbness.
Sunday, June 10, 2018
Mnemonics and basics of ECG interpretation

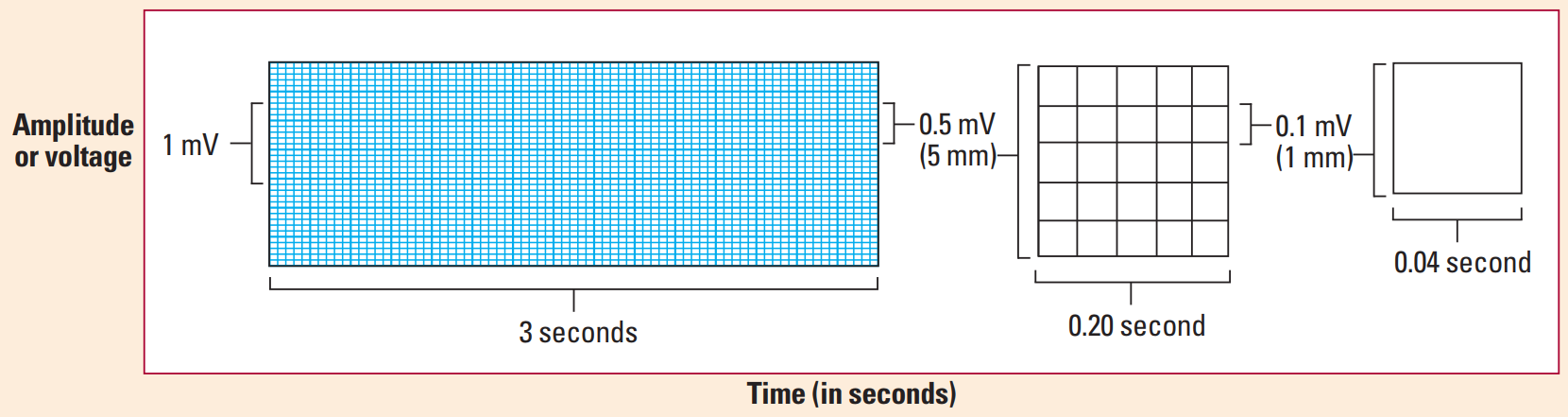
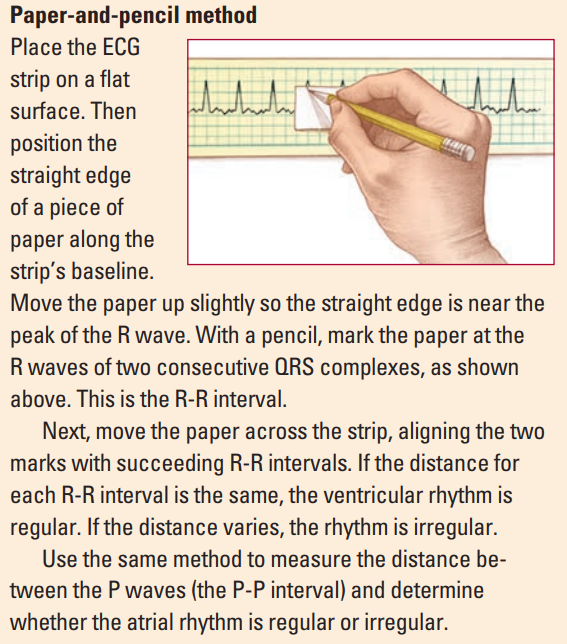
- Use the rythm strip / Lead II and count the number of R waves in 6 seconds (30 large boxes ) and multiply by 10.
-- Due to the variations of the heart rate : The corrected QT interval estimates the QT interval at a heart rate of 60 bpm.
-- The following formula can be used to calculate the QTC = QT interval / √ RR interval (Bazzet's formula)
-- RR interval = 60/Heart rate
-- Note: there are many formulas which can be used for calculation of but this is probably the easiest one.
-- QTc is prolonged if > 0.44 secs in men or > 0.46 secs in women
-- QTc > 500 is associated with increased risk of torsades de pointes



